Hover over the green dots to learn more about a homes roofing system.
Roofing System
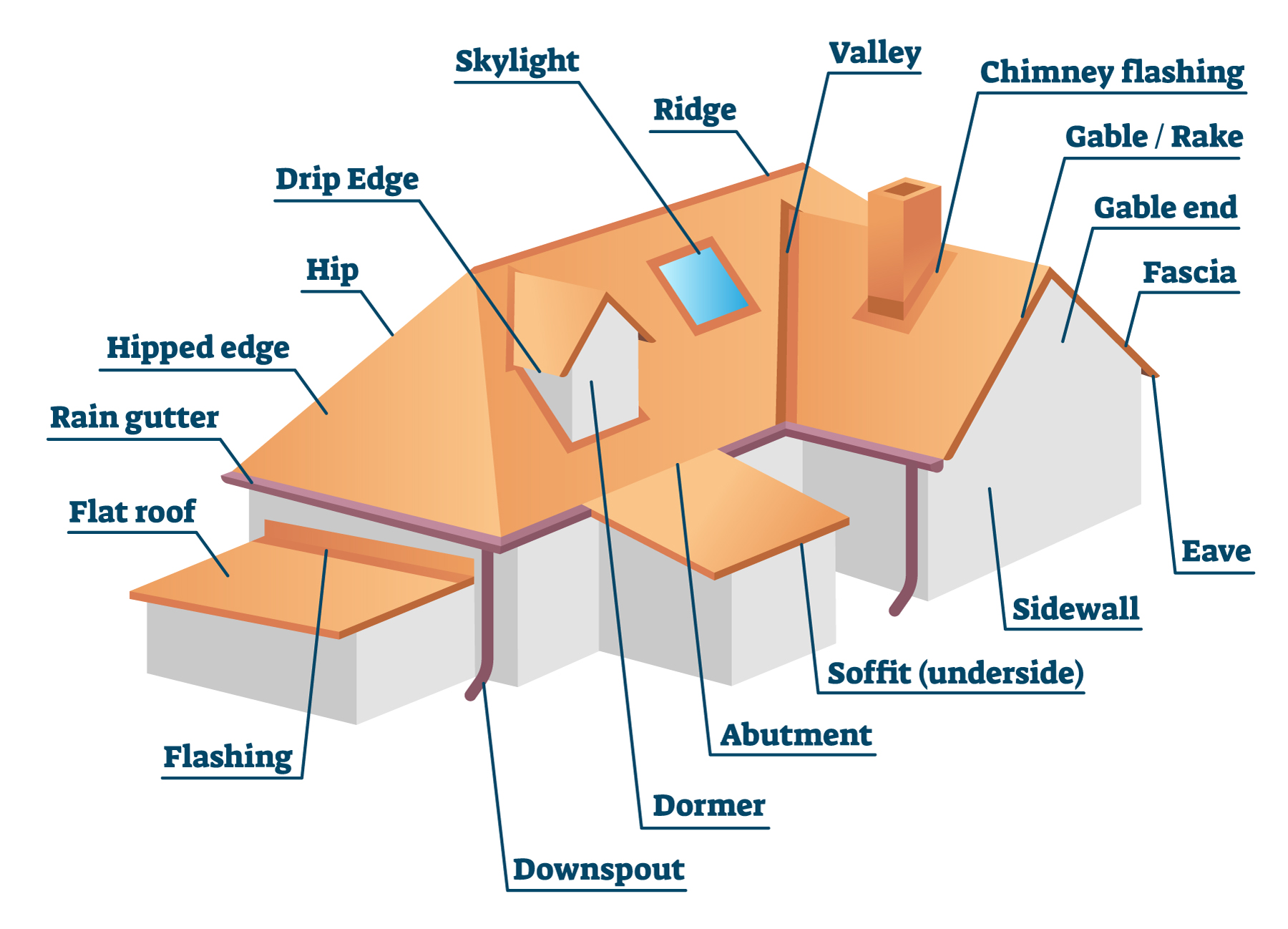


















Types of Roofs:
- Hip with cross gables: a central hip with crossing gables. It will also have valleys.
- Hip and gable or Dutch hip roof: a combination hip and gable where the hip ends partially up the gable.
- Pyramid or hip roof: a roof built on a square or rectangle with a base with eaves the same length. Side opposites of each other will be the same size.
- Gambrel roof: a gable roof with breaks in the planes commonly found on barns.
- Gable: two pitched roofs, back-to-back, forming a triangular roof. The sides opposite of each other may or may not be the same size. The ridge does not need to be centered; it then becomes a salt box roof.
- Shed: a roof that starts at the eaves of the existing roof and continues at a lower pitch. Most patio covers are shed roofs.
- Hip on gable: a partial hip starts the lower section unusually about half way up. The roof then transforms into a small gable roof. It looks like a gable roof sitting on top of a hip roof.
- Cross gable roof: pairs of gable roofs set a right angle to each other. Dormers often create cross gable roofs. The cross appears when looking down into the roof.
- Mansard: a couple planed hip roof. Very steep on the sides, the sides are used as walls with a hip roof sitting on the top. Looks like a hip roof sitting on top of a gambrel roof.
- Kicked eaves or partridge rail roof: a roof where the plane near the eaves is “kicked” to give the visor effect.
- Hip roof: a gable roof with ends brought together at the same pitch as the rest of the roof.
- Salt box roof: shed roof built onto a gable roof at the same pitch and width.
- Flat roof: a plane that is pitched at a low angle to shed water – 1/12 pitch.
